If your engine is running rough, your fuel economy has dropped, or you’ve failed an emissions test, the culprit could be your EGR valve. The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve is a critical part of your vehicle’s emissions control system—and when it fails, it can cause performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions problems.
In this guide, you’ll learn the most common symptoms of a bad EGR valve, how to diagnose the issue, what causes EGR failure, and what to do about it.
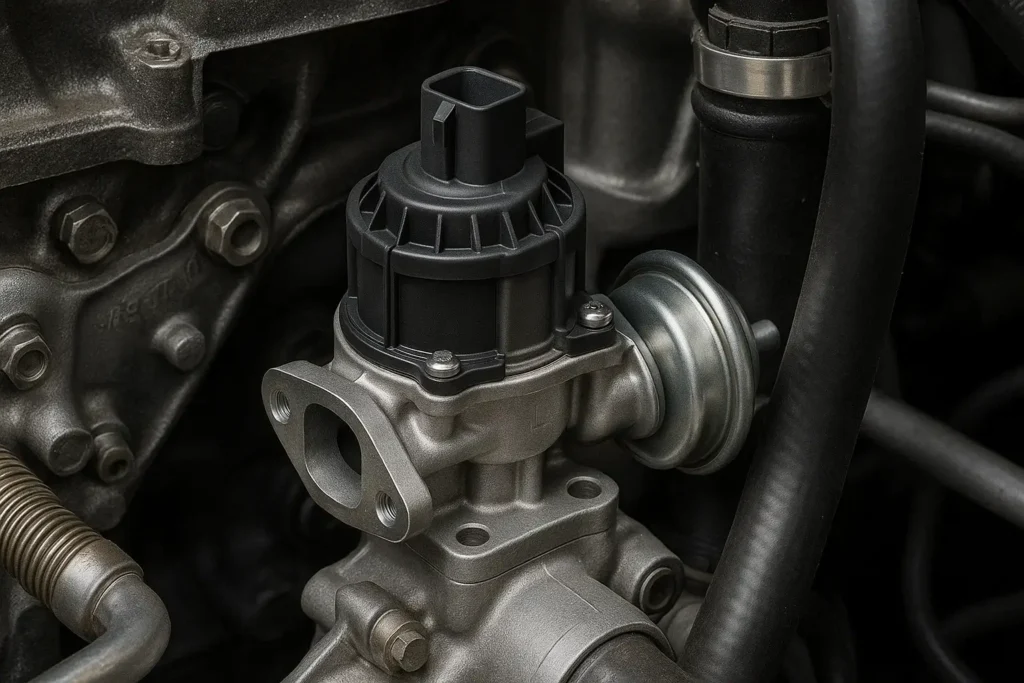
What Does an EGR Valve Do?
The EGR valve helps reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the engine’s intake system. This lowers combustion temperatures, which helps meet emissions standards and improves overall engine efficiency.
Modern vehicles may use pneumatic (vacuum-operated) or electronic EGR valves, depending on the make and model.
What Happens When the EGR Valve Fails?
A failing EGR valve can:
- Get stuck open, allowing too much exhaust gas into the intake, disrupting the air-fuel ratio.
- Get stuck closed, preventing recirculation and causing increased combustion temperatures.
In both cases, this disrupts engine performance and increases emissions, sometimes without any obvious symptoms at first.
Bad EGR Valve Symptoms
Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent more serious engine problems.
1. Rough Idle or Stalling
If your EGR valve is stuck open, it can let too much exhaust into the intake manifold at idle. This can cause:
- Engine hesitation
- Fluctuating RPMs
- Complete stalling when stopped
2. Engine Knocking or Pinging
A stuck-closed EGR valve can increase combustion temperatures, causing pre-ignition (spark knock), especially under load or during acceleration.
This knocking isn’t just annoying it can damage pistons and valves if left untreated.
3. Poor Fuel Economy
With a faulty EGR valve, your engine’s air-fuel mixture may be off. This forces your ECU to compensate by injecting more fuel, which leads to:
- Decreased MPG
- Increased fuel costs
- Rich fuel mixture
4. Check Engine Light (CEL)
A malfunctioning EGR valve often triggers a Check Engine Light. Common OBD-II codes include:
- P0401 – EGR flow insufficient
- P0402 – EGR flow excessive
- P0405 – EGR sensor circuit low
Using a scan tool can help confirm if the EGR valve is at fault.
5. Failed Emissions Test
An EGR valve that doesn’t regulate NOx emissions properly may:
- Cause high NOx output
- Trigger readiness monitor failure
- Lead to a failed smog or emissions inspection
6. Loss of Power or Acceleration
If the EGR system is malfunctioning, you may notice:
- Sluggish throttle response
- Surging or jerking during acceleration
- Reduced engine output
7. Engine Misfires
Erratic air-fuel ratios due to a malfunctioning EGR valve can cause:
- Cylinder misfires
- Rough running
- Trouble codes for ignition or fuel delivery
Other Signs of a Clogged or Failing EGR Valve
EGR valve issues aren’t always easy to spot. Here are less obvious indicators:
• Sulfur or Fuel Smell From Exhaust
A faulty EGR valve can affect combustion, leading to rotten egg smells from unburned fuel or poor catalytic converter performance.
• Black Smoke From Tailpipe
If your engine runs rich due to an improper EGR flow, it may emit black smoke during acceleration.
• Ticking or Tapping Noise
Excessive carbon buildup in or around the EGR valve may cause unusual noises from the valve or intake system.
What Causes EGR Valve Failure?
• Carbon Buildup
Over time, exhaust soot accumulates inside the valve, restricting movement.
• Vacuum Leaks
In vacuum-operated EGR systems, a cracked or brittle vacuum line can prevent proper valve operation.
• Electrical Failure
In electronically controlled systems, a faulty solenoid or position sensor can trigger failure.
• Oil or Moisture Contamination
Oil blow-by or moisture intrusion can gum up internal parts and connectors.
How to Diagnose a Bad EGR Valve
Diagnosing an EGR valve issue requires a mix of visual inspection and basic testing.
Visual Inspection
- Remove the EGR valve and check for carbon deposits
- Inspect vacuum lines or wiring harnesses
- Look for cracked gaskets or carbon leakage around the mounting base
Multimeter Testing (Electronic Valves)
- Check for proper voltage at the connector
- Use a scan tool to monitor the valve’s position data (if available)
Vacuum Testing (Mechanical Valves)
- Apply vacuum to the valve with a handheld pump
- If idle changes when vacuum is applied, the valve may be functional
OBD-II Diagnostic Tools
- Read and clear codes
- Review freeze-frame data to see when the EGR fault occurred
How to Fix a Bad EGR Valve
Clean the EGR Valve
If the issue is carbon buildup, you may be able to:
- Remove and soak the valve in carb or EGR cleaner
- Use a wire brush to remove stubborn deposits
- Clean related ports and passages
Estimated cost: $5–$15 for cleaner
Replace the EGR Valve
If the valve is electronically or mechanically damaged, replacement is necessary.
- Part cost: $70–$400+
- Labor: 1–2 hours
- Total replacement cost: $150–$600, depending on vehicle
Clear the Check Engine Light
After repair, use a scan tool to reset the codes. Drive the vehicle to allow the readiness monitors to reset.
Can You Drive With a Bad EGR Valve?
Short answer: Yes, but not for long.
Driving with a faulty EGR valve can lead to:
- Increased engine temperatures
- Detonation damage
- Failed emissions test
- Decreased fuel efficiency
If you’re experiencing symptoms, it’s best to diagnose and repair the issue promptly.
How to Prevent EGR Valve Problems
Use Quality Fuel
Top-tier gasoline helps reduce carbon buildup in the combustion chamber and EGR system.
Perform Routine Maintenance
- Clean the EGR valve and passages every 50,000–100,000 miles
- Replace clogged air filters that can impact combustion quality
Address Vacuum or Sensor Issues Early
Fixing a vacuum leak or replacing a failing DPFE sensor (in Ford systems) can prevent long-term damage to the EGR valve.
Conclusion
A failing EGR valve can quietly damage your engine and hurt performance without warning. By recognizing the bad EGR valve symptoms, you can:
- Prevent costly engine repairs
- Improve fuel economy
- Pass emissions tests
- Keep your vehicle running smoothly
If you’re unsure, use a scan tool or consult a trusted mechanic to properly diagnose the issue.
FAQs
Can I drive with a bad EGR valve?
Technically, yes—you can drive with a bad EGR valve for a short time. But it’s not a good idea. A malfunctioning valve affects the engine’s air-fuel mix, which can lead to higher emissions and long-term damage to your engine if ignored.
Will a bad EGR valve cause my car to fail emissions?
Yes, it absolutely can. The EGR valve plays a key role in controlling emissions by recirculating exhaust gases. If it's not working properly, your car may release excess nitrogen oxides and fail an emissions test.
How do I test if my EGR valve is bad?
There are a few ways to check. Mechanics often use a vacuum gauge or scan tool to diagnose issues. You can also look for physical signs like a rough idle or hesitation when accelerating. A clogged or stuck valve can usually be confirmed with a proper inspection.
How much does it cost to fix or replace an EGR valve?
The price can vary depending on your vehicle and where you get the repair done. On average, expect to pay anywhere from $150 to $500, including labor. Some valves can be cleaned instead of replaced, which might save you money if the issue isn’t too severe.



