The fuel pressure regulator is a small but vital component of your vehicle’s fuel system. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the right pressure in your fuel system, ensuring optimal engine performance. When it fails, it can cause a wide range of issues, from poor performance to significant engine damage.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key symptoms of a failing fuel pressure regulator, explain how to diagnose the problem, and provide steps to address it. Whether you’re a seasoned car enthusiast or a novice, this article will help you understand what to look out for and how to take action before things get worse.
What Is a Fuel Pressure Regulator and Why Is It Important?
This is a crucial component in your vehicle’s fuel system that ensures the fuel injectors receive the correct pressure for proper combustion. If the fuel pressure is too high or too low, it can cause a range of engine performance issues, such as poor fuel efficiency, rough idling, or stalling.
How a Fuel Pressure Regulator Works
The regulator controls the fuel pressure in the fuel rail, allowing the engine to receive consistent fuel flow regardless of driving conditions. As you accelerate, the engine demands more fuel, and the regulator adjusts to maintain the correct pressure. When the engine is idling or at low speeds, the regulator keeps the pressure lower to prevent over-fueling.
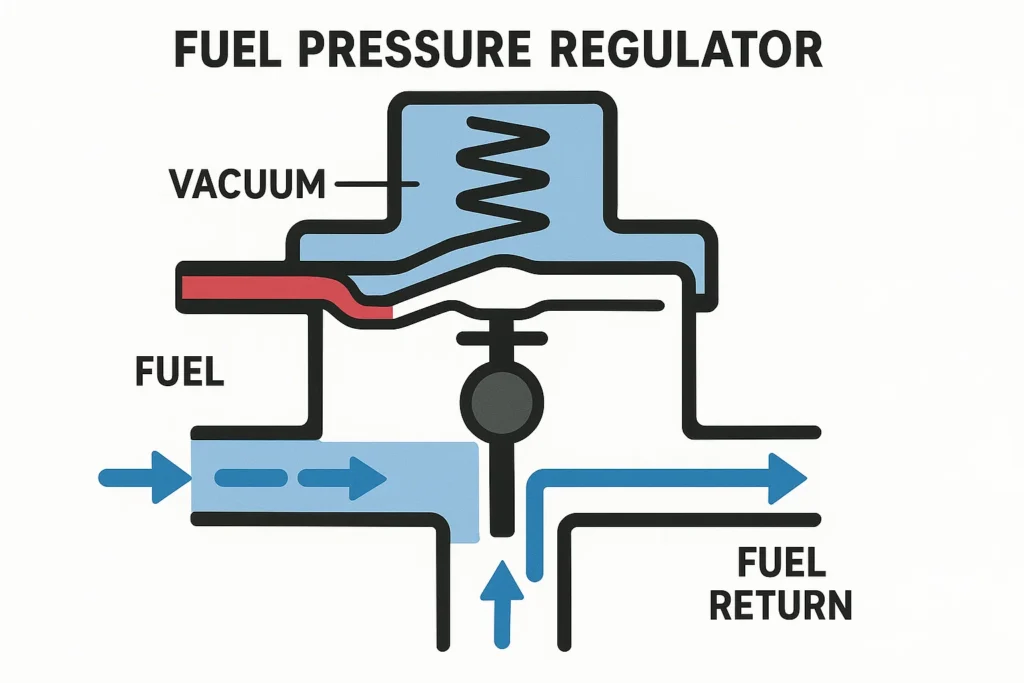
Common Location of the Fuel Pressure Regulator
In most vehicles, it is located either on the fuel rail near the injectors or on the fuel line near the fuel tank. Its exact position may vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
Key Symptoms of a Failing Fuel Pressure Regulator
Recognizing the symptoms of a faulty fuel pressure regulator early on can save you from costly repairs and potential engine damage. Here are the most common signs that it may be failing:
1. Poor Engine Performance and Hesitation
A malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator can cause your engine to hesitate or stumble during acceleration. You may feel a loss of power, or the car may struggle to respond when you press the gas pedal.
- Potential Causes: Inconsistent fuel pressure can lead to poor combustion, causing hesitation or stuttering in the engine.
- Diagnostic Steps: If your engine hesitates, check the fuel pressure using a gauge. If it’s too high or too low, it’s a clear sign that it is malfunctioning.
2. Engine Stalling or Rough Idling
If your engine stalls or idles roughly, especially at low RPMs, it could be a sign of a faulty fuel pressure regulator. A bad regulator may cause the engine to receive inconsistent fuel flow, leading to poor idle quality and stalling.
- Potential Causes: Fuel pressure fluctuations can cause the engine to stall or run erratically at idle.
- Diagnostic Steps: Watch the idle speed while the engine is running. If it fluctuates or the engine stalls, perform a fuel pressure test to check for abnormalities.
3. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
A failing fuel pressure regulator can cause excess fuel to be delivered to the engine, leading to poor fuel efficiency. If you notice your fuel economy has drastically decreased, this could be a sign that the regulator is malfunctioning and over-feeding the engine with fuel.
- Potential Causes: Excess fuel being delivered to the engine due to high fuel pressure, leading to inefficient combustion.
- Diagnostic Steps: Compare your current fuel efficiency to the vehicle’s manufacturer specifications. If your car is consuming more fuel than expected, test the fuel pressure and compare the results to the normal range.
4. Black Smoke from the Exhaust
Excessive fuel being delivered to the engine can cause it to run “rich,” meaning more fuel than air in the combustion process. This can result in black smoke coming out of the exhaust.
- Potential Causes: Over-fueling due to a malfunctioning fuel regulator that prevents proper fuel pressure regulation.
- Diagnostic Steps: If you notice black smoke from the exhaust, inspect the regulator for signs of damage. An easy way to test is by measuring fuel pressure with a gauge.
5. Fuel Leaks Around Fuel Pressure Regulator
Fuel leaks are a serious safety risk. If your fuel pressure regulator is damaged, it may cause fuel to leak out from around the component. This could lead to a dangerous fire hazard if not addressed quickly.
- Potential Causes: Worn-out seals, cracked regulators, or damaged components in the fuel system.
- Diagnostic Steps: Visually inspect the regulator and surrounding fuel lines for any signs of leaks. If you see fuel pooling or smell gasoline, take immediate action to replace the regulator.
6. Check Engine Light (CEL) or Error Codes
A malfunctioning regulator can trigger the Check Engine Light (CEL), often accompanied by error codes related to fuel pressure. Common codes associated with a bad regulator include P0087 (fuel rail/system pressure too low) and P0455 (evaporative emissions leak).
- Potential Causes: A faulty regulator can cause pressure irregularities that the vehicle’s computer detects.
- Diagnostic Steps: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any error codes. If the codes indicate fuel pressure issues, the regulator may need to be replaced.
How to Diagnose a Faulty Regulator?
Proper diagnosis is key to determining if the fuel pressure regulator is the cause of the problem. Here’s how you can test for a faulty regulator:
1. Testing Fuel Pressure with a Gauge
- Method: Connect a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail or regulator port.
- Ideal Pressure Range: Compare the reading with the manufacturer’s specifications for fuel pressure. If the reading is too high or low, it indicates a problem with the regulator.
2. Visual Inspection for Leaks or Damage
- Method: Inspect the fuel pressure regulator and surrounding fuel lines for visible damage, cracks, or leaks.
- Symptoms of Failure: Fuel or vapor leaking around the regulator is a clear sign that it needs to be replaced.
3. Checking for Vacuum Leaks
- Method: Inspect the vacuum lines connected to the regulator for cracks or disconnections.
- Symptoms of Failure: A vacuum leak can prevent the regulator from adjusting fuel pressure properly, causing rough idling or stalling.
4. OBD-II Diagnostic Scan
- Method: Scan the OBD-II system for any fuel system-related error codes, such as P0087 or P0455.
- Symptoms of Failure: These codes can indicate issues with fuel pressure regulation and can help pinpoint the regulator as the culprit.
What Causes its Failures?
Understanding the causes of fuel pressure regulator failures can help prevent future problems. Common causes include:
1. Age and Wear of the Regulator
Over time, internal components like seals and diaphragms can wear out, causing the regulator to lose its ability to maintain consistent fuel pressure.
2. Contaminated Fuel
Dirt, debris, or water in the fuel can damage the fuel regulator, leading to inconsistent fuel pressure or complete failure.
3. Fuel Pump Issues
A malfunctioning fuel pump can cause excessive or fluctuating fuel pressure, which may eventually damage the regulator.
4. Faulty Vacuum Lines
Cracked or disconnected vacuum hoses can prevent the regulator from functioning properly, causing irregular engine performance.
When to Replace the Fuel Pressure Regulator
If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly to avoid further engine damage. Replacing it may be necessary if:
- The regulator is visibly damaged or leaking
- Fuel pressure readings are out of specification
- Symptoms persist even after addressing other fuel system issues
DIY vs. Professional Replacement
If you’re comfortable with basic tools and mechanical work, you can replace the regulator yourself by following the manufacturer’s guidelines. However, if you’re unsure about diagnosing or repairing the issue, it’s best to seek professional assistance.
Preventing Fuel Pressure Regulator Issues
To extend the life of your fuel regulator and keep your fuel system in top condition, consider the following preventive tips:
1. Regular Fuel System Maintenance
- Replace fuel filters on time
- Use high-quality fuel from reputable stations
- Regularly inspect fuel lines and connectors for wear
2. Avoiding Fuel Contamination
- Keep your fuel tank at least a quarter full to prevent sediment buildup
- Use fuel additives to keep the system clean
Conclusion
The fuel pressure regulator is a crucial part of your vehicle’s fuel system, and ignoring symptoms of failure can lead to poor performance and expensive repairs. By recognizing the signs of a failing regulator and taking quick action, you can keep your engine running smoothly and efficiently.
If you notice any of the symptoms discussed in this post, don’t hesitate to diagnose the issue. Early intervention can save you from costly repairs and keep your vehicle in optimal condition.



